
Cold in Elderly: Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment Options
Never pass by a cold in elderly easily. Most elderly people are at serious risk due to their weak immune systems. As they age, the physiological conditions of the elderly become more sensitive and fragile. Perhaps we can even use this example that the elderly are more similar to infants and children in terms of vulnerability. For this reason, the elderly need more careful and regular care. Caring for elderly in cold weather and winter prevents them from getting sick.
This care increases with the onset of autumn and the decrease in temperature and changes in weather conditions. In this season, it is necessary for the elderly and their families to be aware of important health and care tips. Preventing cold in the elderly will allow them to enjoy the pleasant autumn weather and have a happy season instead of getting sick and injured.
Do you know the principles of cold weather safety for older adults? In this article from the Human Health Mag website, we would like to discuss the common cold in elderly, its symptoms, causes, prevention & treatment methods, and complications of common cold in older adults.
What Is a Cold and Why Is It Important to Care for Seniors with a Cold?
The common cold is also known as nasopharyngitis, rhinopharyngitis, and acute coryza. This contagious disease involves the upper respiratory tract, mainly affecting the nose. Symptoms of a common cold last three to four days, and the most common symptoms are: sore throat, stuffy nose, runny nose, cough, sneezing, and pain in the hands and feet, and sometimes fever. If symptoms persist for more than a week and are accompanied by severe headache, weakness, and loss of appetite, the person most likely has the flu.
Cold are more important in seniors because their immune systems are weaker and their bodies are less able to fight off the disease. The likelihood of catching a cold is higher in cold seasons, and as a result, this probability is even higher in the elderly and young children. Due to their physiological conditions and weakened bodies, the elderly are more sensitive to the cold virus, and their immune system is less resistant than younger people. Therefore, the first and most important measure for the elderly is to prevent cold.
Preventing and caring for the elderly from cold is very important, because their immune systems are weaker and they may suffer from more serious complications. Also, in case of infection, timely medical and home treatments are very important for the elderly to recover as quickly as possible. There are several recommendations for caring for the elderly with cold, such as consuming foods rich in vitamins, getting enough rest and sleep, drinking fluids, maintaining hygiene, medical care, etc., which we will discuss in more detail below.

What Are the Common Symptoms of a Cold in Older Adults?
Cold symptoms in the elderly may be similar to those in younger people, but due to their weakened immune systems, these symptoms may be more severe and last longer. Due to the high risk of complications, special care and attention is necessary for elderly people with a cold. Cold in elderly usually begin with the following symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Feeling cold
- Weakness
- Congestion and runny nose
- Dry cough or cough with phlegm and sneezing
- Sore throat and inflammation of the throat
- Fever
- Muscle and joint pain
- Headache and a feeling of heaviness in the head
- Watery eyes
- Aches and pains
Cold Warning Signs That Need a Doctor’s Visit
In older adults, some cold symptoms can indicate more serious problems and require immediate medical attention. These warning signs include:
- A fever of 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius) that lasts more than a few days
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- Chest pain or tightness, which could be a sign of heart or lung problems
- A cough that is severe or lasts more than a few weeks
- Any sudden change in mental status, such as confusion or unusual drowsiness
- Symptoms such as dry mouth, decreased urination, or dizziness
- Extreme weakness or fatigue that prevents you from doing daily activities
- If cold symptoms last more than 10 days or get worse
Why Do Elderly People Get Cold So Easily?
The elderly are more susceptible to colds for various reasons. Some of these reasons include:
- Weak immune system and less ability to fight viruses and infections
- Chronic underlying diseases such as diabetes, heart and lung diseases
- Use of certain medications
- Poor nutrition and vitamin and mineral deficiencies
- Decreased physical activity in the elderly, general weakness of the body and reduced resistance to diseases
- Stress and anxiety
- Closed and crowded environments that can increase the risk of virus transmission
- Failure to observe personal hygiene and wash hands regularly
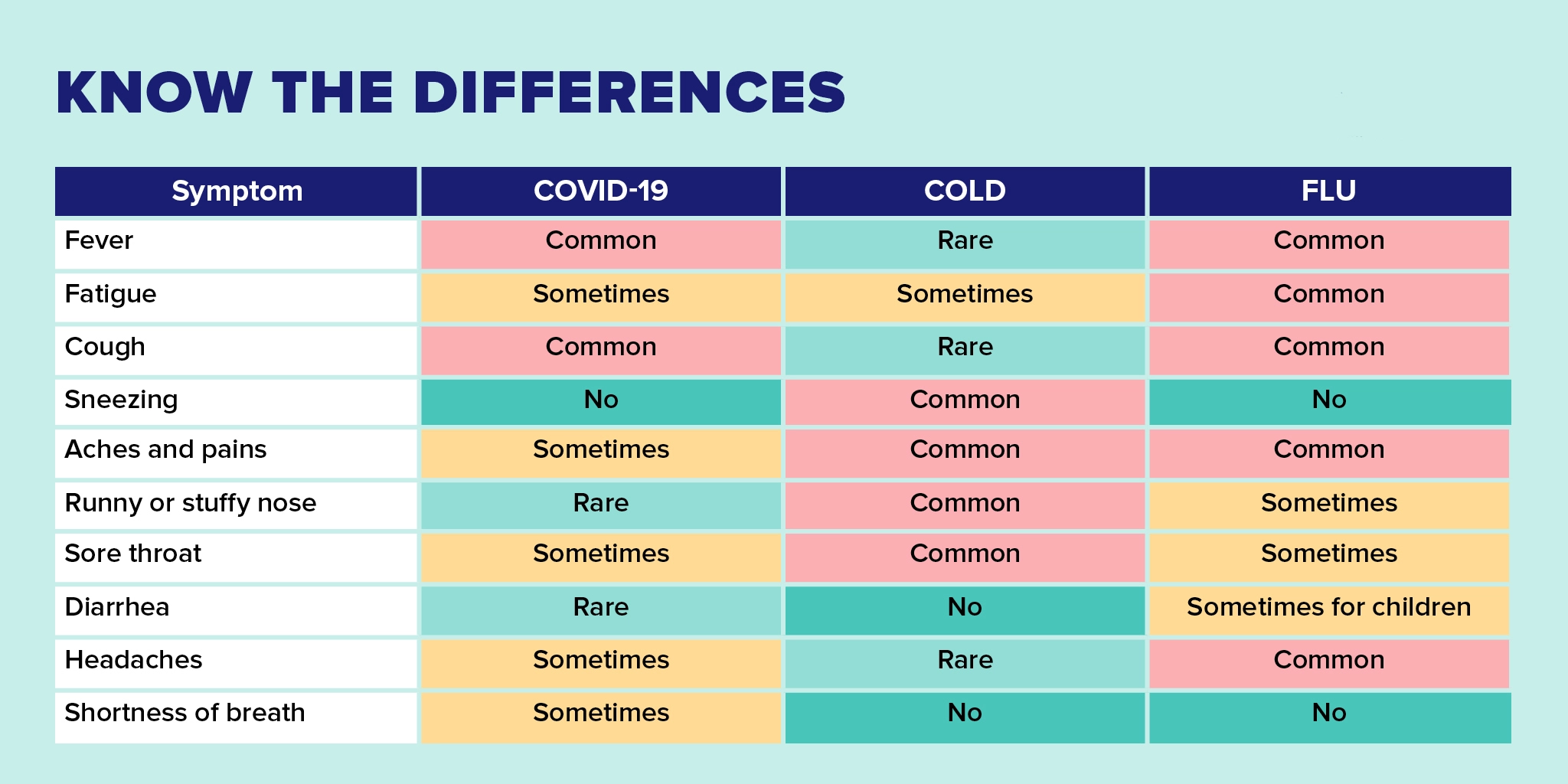
COVID vs. Cold: What’s the Difference?
If you are still unsure whether an elderly person has coronavirus or a cold, the following table can be useful for you. In the table below, we compare the symptoms of Covid-19 with the common cold. If you are still in doubt with the help of the table below, it is wise to consult a doctor and get a corona test if necessary.
| Symptoms | Coronavirus (covid-19) | Cold |
| Duration of symptoms | 7 to 25 days | Less than 14 days |
| Cough | Common (usually dry) | Common (mild) |
| Wheezing | No | No |
| Dyspnea (Shortness of Breath) | Sometimes | No |
| Chest pain | Sometimes | No |
| Rapid breathing | Sometimes | No |
| Sneezing | No | Common |
| Runny nose | Rare | Common |
| Sore throat | Sometimes | Common |
| Fever | Common | If present, is short-lived |
| Feeling weak and tired | Sometimes | Sometimes |
| Headache | Sometimes | Rare |
| Body aches | Sometimes | Common |
| Diarrhea and vomiting | Sometimes | Rare |
| Chills | Sometimes | No |
| Reduced sense of taste and smell | Sometimes | Rare |

Treatment of Cold in Elderly
One of the annoying symptoms of a cold is sore throat and runny nose. To reduce these symptoms, it is best for the elderly patient to gargle with salt water 3 times a day. Elderly patients with a cold should have absolute rest and lie down until they recover completely. Rest helps a lot to recover physical strength and energy.
On the second and third days, when the patient’s condition is improving, a warm shower can give him a strange relief and reduce the patient’s muscle fatigue. When the patient has a cold, the patient’s body should be warm. Sweating can lead to the release of toxins from the body and speed up the recovery of the disease.
Therapeutic Foods to Improve Cold in Elderly
What foods are useful for curing cold in elderly? What is your opinion? Some foods reduce the symptoms of a cold. The best food for a cold for seniors include:
- Consuming vitamin C to speed up the recovery process of a cold. Oranges, bell peppers, and lemons and limes are sources of vitamin C
- A mixture of lukewarm water, honey, and lemon juice is one of the best effective concoctions for cold that is recommended by all doctors
- Usually, people with cold do not feel like eating, so consuming chicken and vegetable soup can both replace meals and help improve cold
- Elderly people with cold
- usually suffer from dehydration, especially if they take antibiotics under the supervision of a doctor. Therefore, they should drink plenty of fluids. Instead of water, they can use fresh fruit juices, weak tea, lemon juice, honey, and herbal teas.
- To prevent respiratory tract inflammation and cleanse the lungs, they can drink ginger or mint tea.
- Consuming bell peppers for their vitamin C
- Consuming carrots for their beta-carotene
- Consuming pepper and mustard, which open the sinuses and thin the lung secretions.
- Onions
- Consuming green tea and black tea, which contain catechins
- Consuming a mixture of one tablespoon of honey and the juice of half a fresh lemon
- Consuming garlic daily
- Consuming medicinal herbs

What’s the worst thing to Eat When You Have a Cold?
Elderly people should never consume fatty, fried, or fast food when they have a cold. These foods can worsen cold symptoms.
How to Get Rid of a Cold Fast in One Day?
If you have a severe cold despite taking preventive measures, you can treat your cold in one day with the following methods:
- Bathing with warm water
- Eating a proper diet in the morning and rich in vitamins
- Inhalation
- Don’t neglect walking
- Eating at lunch time
- Drinking fluids when you have a cold
- Eating a spicy meal at dinner
- Night shower (it is better to add a few drops of eucalyptus essential oil to the bathtub)
- Get enough sleep and on time
Cold Prevention Tips for Older Adults
Preventing cold in elderly person is essential because of their weakness and reduced physical strength to fight off diseases. The only effective way to prevent cold in an elderly person is to physically prevent the spread of the virus by washing hands and using face masks. Because this disease is caused by many viruses and viruses undergo rapid changes, vaccination is not an appropriate answer. Some other effective ways to prevent colds in the elderly include:
- Maintaining personal hygiene and washing hands regularly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Using a tissue to cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing and disinfecting surface
- Using a mask in public places or when in contact with sick people
- Getting seasonal vaccines such as the flu vaccine
- Eating foods rich in vitamins and nutrients such as vitamin C and zin
- Drinking plenty of water and warm liquids such as soups and herbal tea
- Getting enough rest and sleep
- Avoiding or reducing stress and creating a calm environment
- Exercising regularly and having light physical activities such as walking
- Always keep yourself warm, especially in the cold season, and use a scarf and hat
- Using zinc supplements
- Using vitamin C supplements daily
- Avoid kissing and shaking hands
- Do not use other people’s towels, glasses and other personal items during the illness

Complications of Cold in Elderly
A cold is not a serious illness and only causes a person to feel tired and uncomfortable for a few days. However, if not treated and cared for properly, a cold in the elderly can lead to more serious complications, which are divided into two categories:
Common complications of Cold in Elderly
- Headache and body aches
- Mild fever
- Severe weakness and fatigue
- Secondary infections such as bacterial infections
- Bronchitis and severe cough
- Sinusitis
- Tinnitus in elderly
More Serious Complications of Cold in Elderly
- Pneumonia and breathing problems
- Middle ear infection
- Exacerbation of symptoms of chronic diseases such as lung disease, heart disease, and diabetes
- Asthma
- Pharyngitis
- Cough
- Chronic chest pain
- Bronchitis
- Strep throat
- Hospitalization
What To Do If Seniors Have a Cold?
Due to their physical weakness and weaker immune system, the elderly experience more severe symptoms of the disease and need someone to take good care of them during the illness. Care for the elderly with cold includes checking the patient’s condition and vital signs, taking care of the patient’s hygiene and health, preparing fresh and nutritious foods for the patient, informing and giving the patient the medications prescribed by the doctor, keeping them warm, paying attention to the patient’s fever level, etc.
Maintaining appropriate humidity in the environment, using a humidifier to reduce dryness of the respiratory tract and relieve symptoms, is effective in treating this disease. Also, preparing light and nutritious foods rich in vitamins and nutrients is very effective in treating cold. Coldcan cause severe weakness and fatigue, which may affect the elderly’s ability to perform daily activities. Therefore, helping them in these situations is necessary.
It is better to leave these actions to an experienced and patient elderly nurse so that you can see your loved one get better as soon as possible and not worry about catching a cold.
Concluding Remarks
Cold in elderly usually occur 2 to 3 times a year. This virus does not have severe complications, but the patient may have a weak immune system and may develop infections, respiratory distress, seizures, ear infections, lung infections, etc. after catching a cold. Preventing colds in these people is important in reducing the risk of serious complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and secondary infections due to a weaker immune system.
The important thing is to see a doctor when you have a cold, because by accurately diagnosing the type of infection (viral or bacterial), the doctor can prevent these diseases from worsening during a cold by adjusting medications and special care. Prescribing appropriate medications to reduce cold symptoms such as fever, cough, and sore throat, as well as preventing drug interactions with other medications, is also important.
A cold is a disease where home care is very helpful in relieving the symptoms and improving it. Applying the home remedies mentioned in this article will have significant effects when you are suffering from this disease.
We’ve shared our thoughts and now it’s YOUR turn! Please share your insights in the comments, and let’s start a meaningful discussion that will help others, too!

Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a cold last in seniors?
A cold usually lasts between 7 and 10 days, but symptoms may last up to three weeks in seniors.
What is the difference between a cold and the flu?
A cold usually has milder symptoms, such as a runny nose, sneezing, and sore throat, while the flu is accompanied by a high fever, severe body aches, and fatigue.
How can you prevent a cold in seniors?
Washing your hands regularly, taking vitamins, using a humidifier, and avoiding contact with sick people are some ways to prevent a cold in seniors.
Are home remedies for a cold effective?
Home remedies such as drinking warm fluids, getting enough rest, using a humidifier, and eating nutritious foods can help relieve symptoms.
When should you see a doctor?
If you have severe symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or a high fever.
What should the elderly do to catch cold less?
To prevent colds, wash your hands more often during the cold seasons. This is the best way to break the chain of virus transmission. Avoid crowded public places. Wear warm clothes and open doors and windows from time to time. Do not shake hands or kiss someone with a cold.
