
Presbycusis in The Elderly: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Presbycusis in the elderly is something we believe is common. Many of us unconsciously speak loudly when we meet the elderly. It is imprinted in our minds that the elderly have poor hearing. This is true because the elderly suffer from a phenomenon called presbycusis. The severity of this condition is not the same for all elderly people and not all elderly people have so-called heavy ears.
Age-related hearing loss (or presbycusis) refers to the gradual loss of hearing in both ears. This is a common problem associated with aging. One in three adults over the age of 65 has hearing loss. It is better to know the signs of presbycusis in seniors so as not to annoy them. Keep reading this article from the humanhealthmag website, so that we can answer the question of whether presbycusis is treatable and examine this disease and its symptoms.
What Is the Simple Definition of Presbycusis?
Presbycusis or hearing loss in the elderly is age-related hearing loss. This condition is the gradual loss of hearing in both ears. Presbycusis is a common problem related to aging. Presbycusis is a gradual and progressive loss of sensorineural hearing loss. This condition affects both ears equally. The onset of presbycusis is usually from the age of 50.
What is presbycusis in the elderly? In people with presbycusis, sounds in the lower frequency range are heard more difficult than low-frequency sounds. This problem affects the understanding and recognition of words by elderly people. The person hears sounds but does not recognize and differentiate them. This problem is more common in the elderly in noisy environments.
What Age Do People Get Presbycusis?
According to statistics, one in three people over the age of 65 has premature hearing loss. Due to the gradual change in hearing, some people are not aware of the changes in their hearing at first. Presbycusis often affects the ability to hear high-pitched sounds, such as telephone rings or microwave beeps. This complication usually does not affect the ability to hear low-pitched and bass sounds.

What Causes Hearing Loss or Presbycusis in Seniors?
You may be wondering what causes presbycusis in the elderly? There are many possible causes of hearing loss in the elderly, most often changes in the inner ear (most common), the middle ear, and along the nerve pathways to the brain. Auditory nerve damage in the elderly has a variety of causes, but the most common factors that cause age-related hearing loss (ARHL) / presbycusis are:
- Heredity and genetics
- Smoking
- Diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes
- Loss of sensory receptors in the inner ear or hair cells
- Reaction to side effects of certain medications, such as aspirin and some antibiotics
- Continuous exposure to loud noise (such as music or work-related noise)
- Aging
Which Symptom Is Present in An Older Adult with Presbycusis?
Recognize the signs of senile hearing loss in the elderly. Presbycusis in the elderly is not accompanied by pain and cannot be seen. Many people cannot understand that an elderly person has hearing problems. The numerous symptoms of senile presbycusis make it easy to recognize this condition. The most important symptoms of slow loss of hearing in both ears in the elderly are as follows:
- Tinnitus, a ringing sound in the ears that may occur in one or both ears.
- It is difficult for a person to understand conversations, especially when there is background noise.
- Some sounds seem too loud and annoying.
- The speech of others seems slow and indistinct or unclear.
- It is difficult to distinguish high and low sounds such as “s” and “z”.
- Men’s voices are easier to hear than women’s. (Men’s voices are low and women’s voices are low)
How Is Presbycusis in The Elderly Diagnosed?
The symptoms of presbycusis in the elderly may be similar to other medical conditions or problems. It is best to consult an ear specialist for a diagnosis. The healthcare provider you see for an exam will use an otoscope, an instrument used for visual examination, to examine the external ear canal and look at the eardrum. The most common otoscopes used consist of a handle and a head, the head of which has a light source and a low-power magnifying lens.
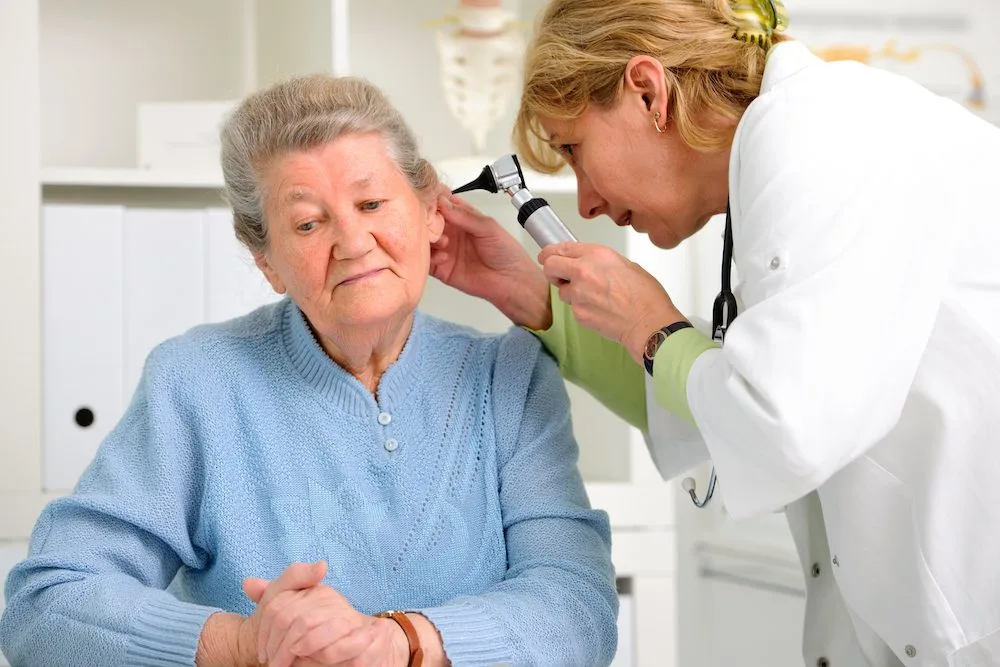

The end of the otoscope head has an attachment for a disposable plastic speculum. The examiner will first flatten the ear canal by pulling on the soft tissue of the ear (usually the earlobe, side or top) and then insert the speculum end of the otoscope into the outer ear. To prevent damage to the ear canal, it is important to place the index or little finger on the head and clamp the hand holding the otoscope against the patient’s head.
The examiner can then look inside the ear canal through the otoscope. This can help him or her detect damage to the eardrum, blockage of the ear canal by foreign objects or earwax, inflammation, or infection.
You may then be referred to a hearing specialist for a hearing test, or audiogram. Sound waves can travel through the ear canal, eardrum, and bones of the middle ear (air conduction) to the inner ear. They can also pass through the bones around and behind the ear (bone conduction).
An audiologist tests your ability to hear sounds. Sounds are distinguished by their loudness (intensity) and the speed at which the sound waves vibrate (pitch). Hearing occurs when sound waves stimulate the nerves in the inner ear, which then travel along nerve pathways to the brain.
An audiogram is a test in which sounds are played through headphones into one ear at a time and you are asked to respond when you hear each sound. If a person cannot hear certain sounds, it indicates that there are signs of hearing loss or presbycusis.
Complications of Presbycusis in The Elderly
Presbycusis in the elderly contributes to the likelihood of cognitive impairment in older people. In people with this condition, the risk of developing dementia increases with age. Several studies confirm the connection between the severity of hearing loss and cognitive impairment, but this relationship is not fully understood.
Hearing affects many aspects of daily life, including communication, safety, and social interaction. For example, hearing loss leads to increased social isolation and decreased independence in older people. There can also be negative effects on mood, such as increased anxiety, depression, and apathy.
High-frequency presbycusis in the elderly can pose serious safety concerns, as it may be difficult for older adults to respond to alarms and signals such as doorbells, telephones, smoke alarms, and traffic lights.
There is evidence of hearing loss and lack of postural control in the elderly, which may be related to the perception of movement and one’s position in space. A deeper understanding of this relationship may have a significant impact on the frequency of loss of balance in elderly, which is a significant factor in the complications of presbycusis and mortality in the elderly.
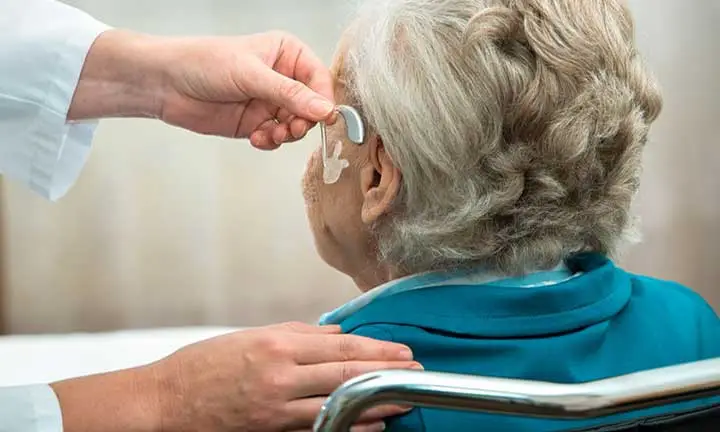
Treatment of Presbycusis in The Elderly
What is the best treatment for presbycusis? In cases of tinnitus, sedatives and vitamins are prescribed, but there is no specific medicine to treat hearing loss or presbycusis in the elderly in the elderly. Unfortunately, old age hearing loss in the elderly is irreversible. When people have problems with their social communication, they are prescribed hearing aids.
Hearing aids keep the brain healthier and improve the elderly’s verbal communication with others. Peripheral devices such as telephone amplifiers or technology that converts speech into text, speech reading training (using visual cues to read speech), and techniques to remove excess wax and prevent excess hair growth in the outer ear are among the methods of old age hearing loss treatment.
Home Treatment for Presbycusis in The Elderly
Garlic has always had a special place among the methods of treating presbycusis in traditional medicine and home remedies. In this section of the article, we will teach you a wonderful treatment for hearing loss. Using this solution improves hearing by up to 87%. Prepare it and pour two drops into your ears.
To prepare the oil for improving presbycusis in the elderly, wash the garlic and crush it well. Before crushing, add olive oil to it. Separate the dissolved oil from the garlic with the help of a strainer and pour the resulting liquid into a dropper. Let the prepared oil stay in the container for a day so that it works better with a complete mixture and use it after a day. Put two or three drops of it in your ear every day and you will notice that your hearing will improve day by day.
Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Prevention and Treatment of Presbycusis
How to improve hearing loss in old age? In the following, we introduce medicinal plants that help to strengthen ear health and prevent presbycusis to a great extent.
Ginkgo biloba
Ginkgo is one of the oldest plants in the world, dating back more than 150 million years. Supplementing this plant has several properties, including increasing memory and preventing forgetfulness. Another property of this plant is increasing blood circulation in the brain, which has many benefits for the whole body, including the ears.
Mint Leaf
Mint is one of the plants that has a high amount of iron and folic acid. Folic acid is effective in ear health, and according to research, hearing loss can be associated with low levels of folic acid in the body. To strengthen your hearing, you can consume mint in dried form in your foods or as a tea.
Dill and Turmeric
For the herbal treatment of presbycusis in the elderly, don’t forget dill and turmeric. Dill is rich in zinc, which affects hearing health, and turmeric also contains a lot of potassium, which the hearing system and ears need this vital element.
Onion Juice
Onion juice has a great effect on reducing infections and resolving ear problems. If you drink a tablespoon of onion juice every morning, noon and night and put a drop of it in your ear, it can help improve your hearing.
Another method is to chop a small onion and put it in a bowl. Put it in the microwave for a few seconds and after removing it from the microwave, let it cool. Then take the onion juice and dilute it with a little water and put two to three drops of it in your ear. 5 minutes is enough to keep it and then you should remove the onion juice from your ear by turning your head.
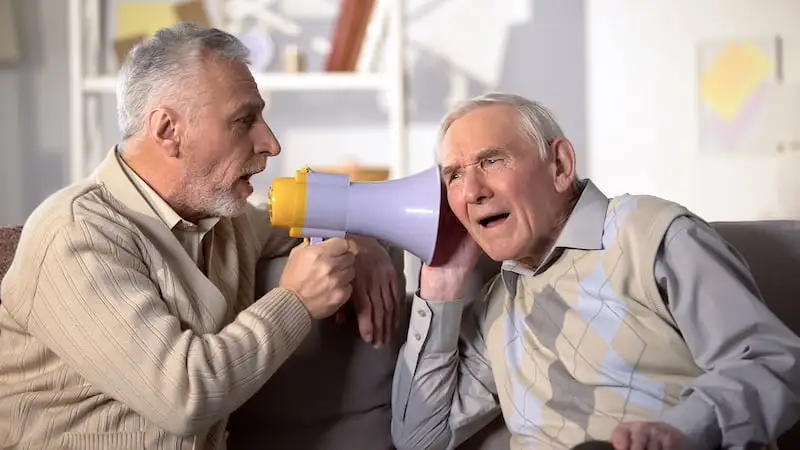

Tips for Talking to People with Hearing Loss
When talking, it is better to have the light shine directly on you. In this case, your facial expressions, lip movements, and body movements are understandable for the person.
- Speak louder than usual, but do not shout. Shouting changes the rhythm of speech.
- In restaurants or events, choose a seat that is away from noise
- If the person does not understand what you are saying, express yourself in shorter and simpler sentences
- When talking to a person with presbycusis, speak at a natural pace
- Stand so that he or she can see your face when you speak
- Do not talk to him or her when you have your hand covering your mouth
- Turn off the radio and TV while talking
- Do not talk to him or her while eating
Recommendations for Caring for the Elderly with Presbycusis
If you want to be successful in managing presbycusis in the elderly, consider the following recommendations.
- Avoid going to places where there is a lot of noise
- Elderly people with presbycusis have a lower level of social security
- The elderly should avoid inserting objects such as pins, pen tips, and even cotton swabs into the ear
- When elderly bathing, avoid inserting cotton swabs into the ear canal and washing it with soap and shampoo
- Do not use cotton swabs to dry the ear canal after bathing. Cotton swabs cause accumulation and compression of the ear canal, and in addition, the cotton tip may remain inside the ear canal.
Concluding Remarks
Presbycusis in the elderly is a progressive hearing loss in both ears and is a common problem associated with aging. Hearing aids are the primary treatment option for this condition and have been shown to have a significant positive impact on the quality of life and communication of hearing impaired people. Remember that hearing aids do not correct hearing problems; their role is to amplify surrounding sounds.
However, presbycusis is a condition that can be controlled and treated with proper care. Also, preventive measures can play a significant role in preventing this condition. Given that presbycusis affects most people, you can be largely successful in preventing this condition with the above recommendations.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is presbycusis in the elderly curable?
Yes, aging can be treated with various treatments, including traditional medicine solutions.
Does presbycusis occur in young people?
Yes, presbycusis can also occur in young people, although it is less common than in the elderly.
What can be done to prevent presbycusis?
Vitamins play a vital role in maintaining ear health and can be effective in preventing presbycusis.
What is the main cause of presbycusis?
More than anything, we should consider changes in the inner ear due to aging as the cause of ear aging. Also, changes in the middle ear or complex changes along the nerve pathway from the ear to the brain can be involved in this occurrence of this disease.
What are the symptoms of presbycusis in the elderly?
Difficulty understanding conversations, especially when background noise is present. Hearing men’s voices more easily than women’s, and other symptoms that we have explained in this article.
At what age does presbycusis begin?
The condition can begin in a person’s 30s or 40s and gets worse as they age.
